2022
Predictions
PROTEIN
After age 30, we begin to lose as much as 3-5% muscle mass per decade, with the steepest decline after age 60. Men lose as much as 30% over their lifetimes. Less muscle equals increased weakness and decreased mobility. Yet, the recommended intake for protein doesn’t increase with age, even as our bodies are less and less capable of digesting and holding onto protein stores.
Protein intake itself tends to decline with aging, a condition referred to as "anorexia of aging," as many elderly persons don’t eat regularly enough. And even when enough protein is consumed, it often is in the form of high-fat animal products.
A study published recently in the European Journal of Nutrition put forward recommendations for older adults to consume at least 1.2 g/kgBW (body weight) daily, a higher level than the RDA. This slight increase was found to be able to produce measurable improvements in physical activity, which in turn implied a 6% lower premature mortality rate and a 10% lower mobility disability risk.
Caution: Your protein needs might vary!
Protein Paradox

Plant-based and cell-based proteins are in a race to replace live-animal sources to fill consumers' protein needs. Photo courtesy of: Aleph Farms, Ltd.
By KERRY HUGHES, MS, Contributing Editor
Novel approach
As the experts work toward divining the best strategy for quantifying protein needs across the lifespan, and how to utilize protein to prevent sarcopenia, novel protein sources have been cropping up. In keeping with the plant-based boom, legumes and seeds are dominating the new protein scene. One example, lupin bean protein, could finally be finding its way to our plates on a regular basis.
Although this leguminous protein has been eyed for years as a potential superstar among plant proteins, researchers in Australia have been making important leaps in understanding and overcoming some of the hurdles that have prevented it from taking off, especially the factors of palatability, nutritional profile, and allergenicity.
Australia is a major producer of lupin, with approximately 55% of the global crop. Now, researchers there are using proteomic analysis and extraction method research to take lupin production from being primarily for livestock feed to becoming suitable for the larger human food market.

Sustainable, ecologically responsible protein continues to be an important ingredient for consumers. Photo courtesy of: Alfreds Food Tech, Ltd.
Research is progressing rapidly on commercializing protein from camelina (Camelina sativa), an herbaceous member of the Brassicaceae family and thus a relative of canola, broccoli, cabbage, and mustard. Protein isolates from another Brassicaceae family member, Descurainia sophia (commonly known as sophia), also are being successfully extracted. Researchers have found them to have good potential as functional proteins for foods. Sophia seeds are a high-protein ingredient, weighing in at around 28% protein. Camelina seeds are an even greater concentrated protein source, at 45% protein by weight.
Although conventional soy protein isolates are a mainstay in foods and as food ingredients, concern has been building regarding the sustainability of their production. Soy production is associated with deforestation where both virgin forests and savannas are being converted into agricultural fields to grow soybeans. For this reason, alternatives to soy proteins have been springing up, some with functional advantages, like faba bean protein, which makes a better, creamier tasting protein.
Boomer Vegans
Recent research suggests that a vegan diet might be the best way to preserve muscle in older obese people. When people are young, extra body fat can result in stronger muscles; however, this trend seems to reverse in the elderly. In elderly persons, it has been found that extra body fat results in weaker muscles in obese people than in non-obese people. A key strategy being researched for preserving muscle strength in elders is that of a methionine-restricting diet, such as a vegan diet. Such a diet was found to mimic calorie restriction because, while this amino acid is abundant in a diet involving meat, fish, or dairy, plant proteins generally contain very little of it. So, while higher protein intake could still benefit obese elderly people, plant-based proteins might be the best option.
Chick pea protein is another source seeing a huge expansion in application, as are proteins from seeds more commonly used for their lipid or carbohydrate components. Examples include chia, hemp, and quinoa.
Solutions from the sea
One big protein source predicted to take off in the coming year is seaweed protein. Already popular in Asia, seaweed-based foods are prized for their rich complement of beneficial vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They have an excellent protein content as well, at around 35%.
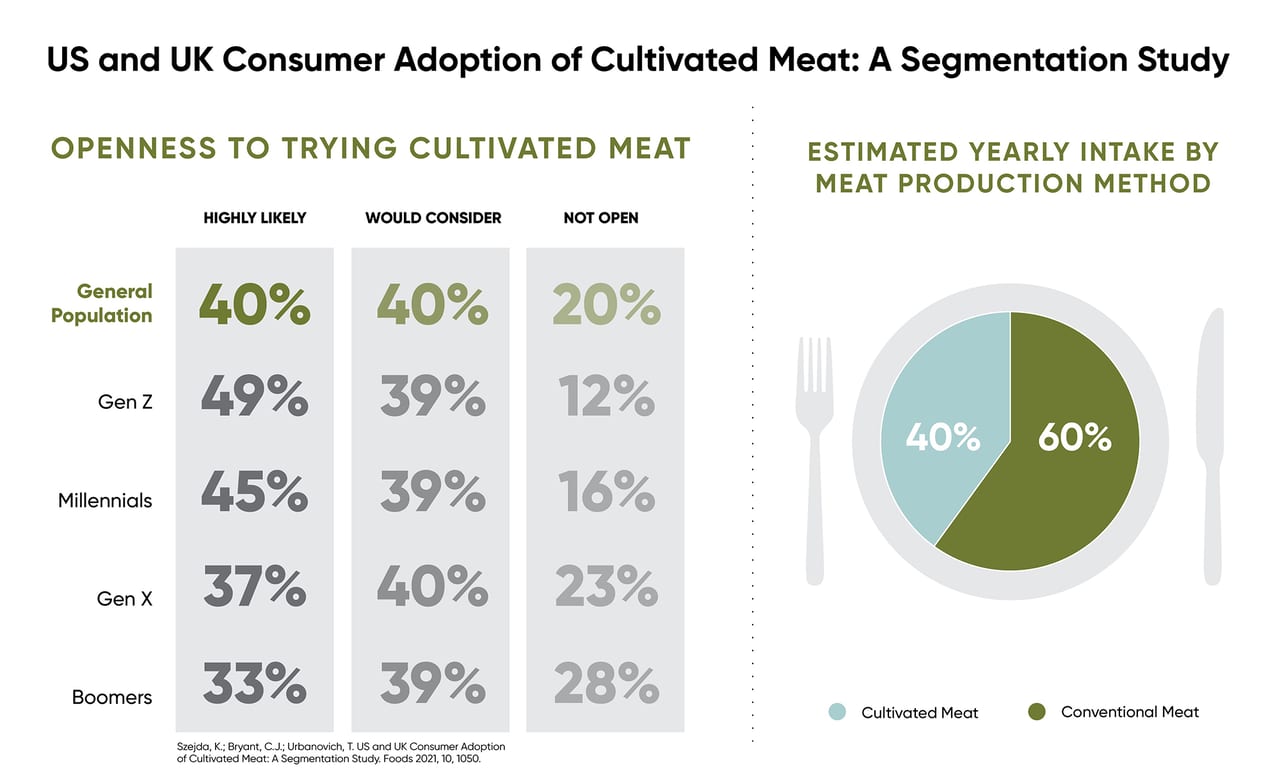
Image courtesy of: Foods Journal/ Keri Szejda, PhD, et alia
High-protein kelp noodles have recently hit some higher-end US supermarkets, indicating that a move into the mainstream could be around the corner. As kelp is a source of protein that requires no land for its production, researchers in Tel Aviv have been exploring the potential of this abundant plant to supply protein isolates. Seaweed protein is a high-value, complete protein as well, containing all nine essential amino acids.
Turning to the lab
Among the many new sources of protein making news are animal proteins made from cultured cells derived from animals, aka “cell-based protein” or “lab-grown protein.” Although the lab-grown meats in production have yet to attain scalabilty, in the past year a number of companies have jumped in, and progress has been rapid.
Made For You
As supplement and nutrition advice increasingly turns to personalization, it makes sense that personalized protein intakes wouldn’t be far behind. Certain populations, such as athletes, women who are pregnant or nursing, persons engaging in hard physical labor or sports needing injury prevention, and people on certain weight loss programs already have more personalized protein requirements.
In the quest for personalization and optimizing protein utilization as we age, a new computational tool supported by the National Institute on Aging is emerging that calculates protein turnover rates from mass spectrometry analysis of metabolic labeling experiments. With these new approaches to proteomics, we will have age-related insights that can help us better understand age-related disease, how to measure protein loss accurately, and how to calculate protein turnover rates.
Some groups express concern, focusing on issues ranging from potential labeling differentiation between lab-grown meat and meat from slaughtered livestock as well as the potential for controlling the safety of manufacture once products do reach full production. Allergenicity issues also could require further exploration.
“If a food contains any lab-grown animal protein, we believe this information should be clearly communicated on the front of the package, and that no animal-raising claims such as ‘humane’ or ‘sustainable’ should be allowed,” suggests Emily Moose, executive director of A Greener World, a non-profit certifier of the world’s top animal welfare label, “Certified Animal Welfare/Approved by AGW.”


Researchers have found that using ultrasonic-assisted extraction instead of the more common alkaline extraction technique to derive protein from a raw source is a more effective process. The method produces proteins with better solubility, water-holding, and oil-absorption capacities, as well as increased foaming and emulsifying properties.
“Honest labeling is critical,” continues Moose, “not only from a transparency, food safety, and allergenicity perspective, but also so that people can choose to support the kind of food production systems they really want, and deliver the change we need.”
Last year, more than $3B was channelled into concerns dedicated to plant-derived proteins and cell-based meat, seafood, and poultry proteins, as reported by The Good Food Institute (GFI). Of the latter, lab-grown fish protein has advanced to where scale production is expected by the end of 2022 or early 2023. While the undertaking was equally massive in terms of technology and challenges, cellular aquaculture has proven to have an edge over lab-grown beef or poultry protein in that the structure of fish muscle tissue lends itself better to the culturing technology.
Something all these new protein sources promise, but are still a ways from delivering, is to ease the burden on the planet’s resources. to ease the burden on the planet’s resources. While the number and variety of protein sources expand, each source is unique in its flavor, texture, and nutrition profiles. Product developers will benefit from working with ingredient suppliers to find the best protein sources for their formulations. PF
Regular contributor Kerry Hughes, MS, principal for EthnoPharm, is an ethnobotanist, herbalist, and author with a 20-year record of success in natural product development. EthnoPharm specializes in global natural product development and education, innovative product formulation, nexus-of-market opportunity identification, expanding the boundaries of new product development, catalyzing applied phyto-product breakthroughs, and bringing to market new, efficacious, and profitable products that not only heal people but help protect the threatened global biodiversity. Contact her at kerry@ethnopharm.com.
December 2021

